The CPU breathes life into your entire computer system. Responsible for all the complex calculations that drive your system together, there’s no computer without this integral part present in your system plugged in the right to the motherboard using a socket.
A dead CPU, though – remains a common theme throughout the troubleshooting world. You’ll often find bent pins and dead of arrival CPUs leading to no POST on your BIOS. However, should you be worried about your dead CPUs damaging other components?
Can A Bad CPU Damage A Motherboard?
No, a bad CPU does not pick up voltage from your motherboard. So, even if it is faulty, it won’t damage your motherboard as it won’t be connected adequately in the first place. Since CPUs don’t discharge any electricity directly to the motherboard, it is the only way for it to get damaged in the first place.
Not grounding the components will also not lead to your CPU damaging a motherboard. So, you are completely safe in every circumstance.
Most CPUs tend to get damaged because of the motherboard and not vice versa. So, there’s a higher likelihood of your motherboard being the likely cause rather than the opposite.
Your motherboard also controls your PSU, which sends the appropriate current and voltage throughout the system. The most probable cause of your motherboard being damaged is an extraneous current supply.
Thankfully, modern PSUs are smart enough to recognize a faulty component and, instead of providing it with an unnecessary amount of voltage/current, shut it down instead.
A point of clarification here is extremely important. An already bad CPU cannot damage your motherboard. But, if you were, say – not grounded properly when installing the CPU to your motherboard, you might end up damaging your motherboard and the entire system even though it won’t be your CPUs fault in the first place.
In essence, the likelihood of a bad CPU damaging a motherboard is highly improbable. In contrast, the opposite is often true. It is considered impossible for a bad CPU to place any harm on your motherboard, given that you install it correctly and do not physically harm the motherboard while doing so.
How To Find Out If A CPU Is Bad?
Your computer is not booting up appropriately, beeping, overheating, or acting unbearably slow are indications of a bad CPU. In essence, erratic behavior that is not of the norm is a sign that your CPU is not working correctly and is bad.
Here are a quick few ways you can find out:
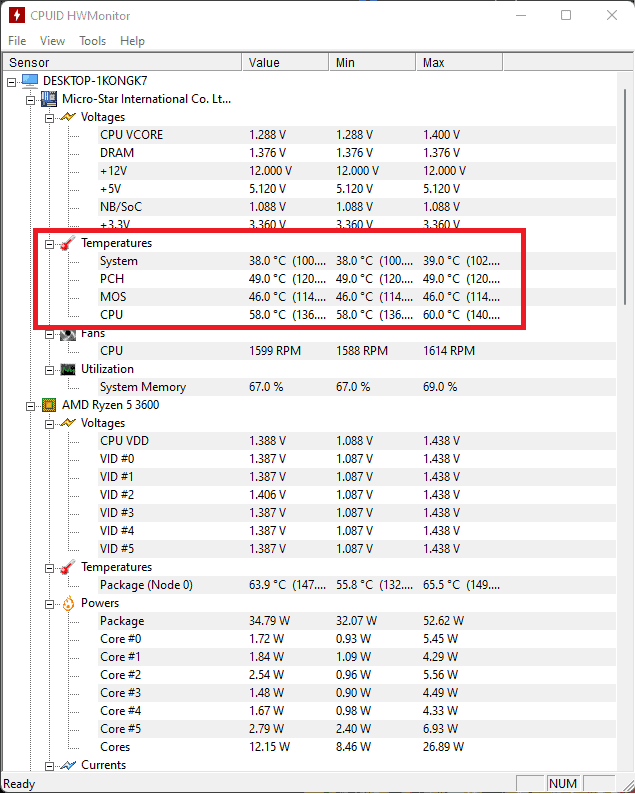
- Temperature Check: Download HWMonitor and take a look at your core temperatures. If you find them to be alarmingly high even after you have checked your cooler temperature – then your CPU is to blame.
- Beeping Noises: If you hear beeping noises after booting your computer and can’t get into Windows, there’s a high chance that an internal component, like your CPU, is malfunctioning.
- BSOD: If you get the all-too-familiar Black Screen Of Death whenever you perform a taxing CPU-intensive task, either your cooling can’t handle the load or your CPU cannot utilize itself to the max.
Moreover, the motherboard does not turn on if the CPU is bad in the first place. It is essentially equal to there being no CPU at all. If that’s the case, the motherboard will not POST until all components are functioning and are connected to it.
This is because POST calls are used to check whether all components are functional and require the CPU for it to present a valid call. So, while hard to decipher – there can be an amplitude of reasons why a POST call doesn’t work. But, if you know that your CPU is faulty, that is the most probable cause.
Can You Fix A Dead CPU?
No, dead CPUs are not fixable in any way or form and will require you to either have them replaced or claim a warranty from their manufacturer. Whether you get a replacement depends on what the damage is.
For example, a bent pin is caused by not properly inserting the CPU into the socket and will therefore not be claimable. But, on the other hand, not booting even after installing the CPU correctly into the motherboard is worthy of a claim.
If you are confused as to how a CPU can be dead in the first place, here’s a quick look at the most probable cause:
- Bent Pins: Installing your CPU in the wrong socket or applying extreme force can lead to delicate pins in your CPU bending, which will permanently damage it.
- Shipper Handling: CPUs are extremely delicate. They must be handled with care. Often, poor packaging from the manufacturer can lead to your CPU arriving DOA (Dead on Arrival)
- Over-Voltage: A Bad PSU or motherboard can fry your CPU. If the voltage going to the CPU is not regulated, and your CPU receives a large number of it, tiny transistors present in the processor will be damaged.
- Extreme Overclocking: When you aren’t sure of the limits of your CPU and want to keep bringing it further with the help of overlocking, you might inadvertently end up killing your CPU in the process.
Since installing a dead CPU on your motherboard will not damage your motherboard at all, you can easily check whether it’s the CPU that is the actual issue in the first place.
You can swap the board out with another and see if you have POST. If that isn’t an option, you can try physically inspecting the processor for any damage (such as bent pins) and hooking up your system with an alternate processor that works.
Takeaway
Problems with your CPU can be annoying to troubleshoot. However, if you are worried about damaging other components along the way, you shouldn’t at all and can continue testing your luck out with other components.
Since the processor only requires such a small amount of voltage/current, it doesn’t have the power to fry other components alongside it anytime soon, especially not the motherboard, as it can sustain a high amount of backflow current due to its redundant and safe design.

Hey, I’m Hammad. I write for this website to help you with the IT advice about PC, RAM, CPU, Motherboard, PSU, and other PC components.
I will provide detailed guides with images, and explain step by step so you can understand the process. Check all my articles here.