Do SSDs get slower over time? This is a question that many people have, especially as they watch their computer’s performance gradually decline over the years. At the same time, some factors can contribute to a decrease in an SSD’s speed, such as overfilling the SSD, external temperature, dust, etc. You can avoid such situations.
For example, you can regularly defragment your drive to help keep it organized and running efficiently. You can also avoid leaving your computer on for extended periods, as this can lead to heat buildup and decreased performance. A few simple steps can help keep your SSD running at its best for many years.
Do SSDs Get Slower Over Time?
SSDs do get slower over time. But it is not because of any mechanical or physical wear and tear. On the contrary, it is due to the gradual accumulation of files over time. The more you will fill your SSD, the more it will cause damage to your SSD.
Every file you create or save on your computer gets stored in a particular location on the disk. So, as more and more files get added, the free space on the disk gets less and less. And the files that are already stored start getting spread out. This process is known as fragmentation.
When your computer has to access a file spread out in different locations, it takes longer to retrieve it. As a result, the performance of your computer slows down.
You can prevent this by regularly defragmenting your drive. Defragmentation is a process of organizing files on your disk so that they are stored contiguously. Then, when your computer needs to access a file, it can do so quickly and without delay.
To defragment your drive, you can use the built-in tool in Windows known as Disk Defragmenter. Simply open the tool and follow the instructions to defragment your drive. Here’s how you can do that:
SSD Defragmentation
- First, go to the Windows search bar, then type defragmentation.
- Select the defragmentation and run as administrator.
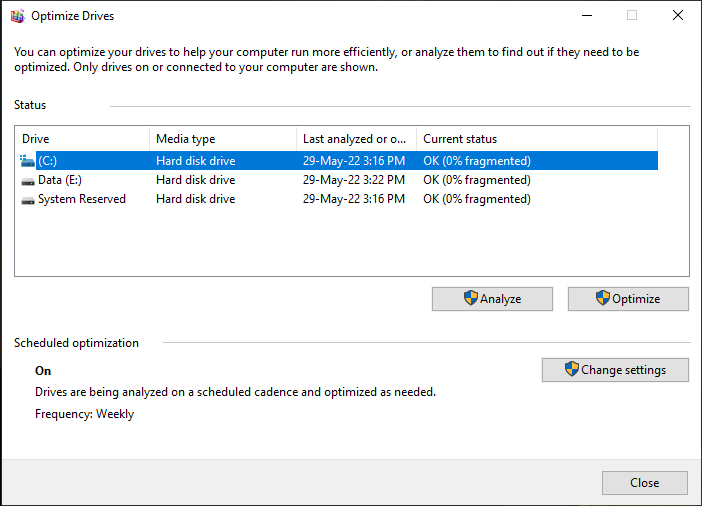
- Now select the drive you want to defragment and press optimize. It will start the process and defragment your drive automatically.
In addition to defragmentation, there are a few other things that you can do to keep your SSD running at its best. One is to avoid leaving your computer on for extended periods. The components tend to get hot when you leave your computer on for long periods. It can lead to decreased performance.
Another thing that you can do is to make sure that your SSD has adequate airflow and ventilation. Proper airflow is necessary to keep the drive cool and prevent heat buildup. You can achieve this by ensuring that there are no obstructions around your computer case and that the case is not blocked off.
Do Larger SSDs Last Longer?
Larger drives have a longer lifespan because they have more capacity to store data. That’s why they don’t have any issue with free space. In addition, it allows the temporary files of the Operating System to be stored in a separate section of the drive. It helps in improving the speed and performance of the drive. So, larger SSDs tend to last longer than smaller ones.
The manufacturers claim the estimated terabytes written (TBW) capacity of an SSD. The estimated data value can be written on an SSD throughout its lifespan. And after the end of TBW, your drive will be dead permanently.
For example, the TBW of a 128GB SSD will be 50 to 100 terabytes. And a 1TB SSD will have 800 to 1600 terabytes. But how often do you write data on your drive? The average computer user writes only 5-10GB of data daily. So, a 128GB SSD should last around 20 years, and a 1TB SSD should last 40 years, but this is not the only factor.
But that’s not the only factor affecting an SSD’s lifespan. So here, we have listed some of them so you can avoid SSD failure.
1. File System and Allocation Unit Size:
The file system is the most important factor affecting any storage device’s life. NTFS is the most common file system used in Windows. It has a default allocation unit size of 4096 KB. A file written to the SSD will be broken down into 4096 KB chunks, and each chunk will be stored in a different location on the drive.
The allocation unit size can be changed to improve performance or to store large files more efficiently. This process increases the lifespan of SSDs.
2. Case External and Internal Environment
Heat kills any computer’s hardware component, including the SSD. An SSD can withstand higher temperatures than an HDD but still has a maximum operating temperature. Therefore, if your SSD is used in a hot environment, it will have a shorter lifespan.
3. Data Type
The type of data you store on your SSD also affects its lifespan. Programs and games are generally static files that don’t change much over time. So they don’t put much wear and tear on the drive. But video and audio files are constantly being read and written as you play or edit them. So it can shorten the lifespan of your SSD.
4. Write Amplification
Write amplification is a phenomenon that occurs in all SSDs. It results from the drive having to write more data than requested. For example, if you write an 8MB file to an SSD, the drive may have to write 16MB or more data to store that 8MB file. This is because the data is stored in blocks much larger than 8MB.
Do SSDs Slow Down as They Approach Full Capacity?
When an SSD starts to fill up, its performance gradually declines. It is because the drive has less free space to work with, and as a result, files get fragmented more easily. In addition, the drive has to work harder to store data in multiple locations, which can also lead to decreased performance.
Keeping your SSD no more than 80% full is important to avoid such a situation. It will help to ensure that there is enough free space for the drive to work with and that files do not get fragmented as easily.
In conclusion, SSDs do get slower over time, but there are several things that you can do to help prevent this from happening. Regular defragmentation, avoiding extended downtime, and keeping your SSD no more than 70% full can help keep your drive running at its best.
How much storage should I keep on my SSD?
You should use 80% of your drive and always keep 20% or more free space. If you are a power user who uses your computer for demanding tasks such as video editing or gaming, you will need more storage than the average user.
You won’t need as much storage if you use your computer for basic tasks such as browsing the web, checking email, and light photo editing.
A good rule of thumb is to keep at least 20% of your SSD free for optimal performance. So, if you have a 128GB SSD, you should keep at least 25GB of free space. It will ensure that your computer has enough room to write new data and that your SSD doesn’t get too full, impacting performance.
If you are unsure how much storage you need, it is best to err on caution and get a larger SSD. You can always add more storage later if you need it.
Conclusion
You can use up to 80% of your drive storage to avoid issues like slowdown drives. A good rule of thumb is to keep at least 20% of your SSD free for optimal performance. Keeping your SSD no more than 80% full can also lead to performance degradation. Therefore, keeping your drive as empty as possible is important if you want it to perform its best.

Hey, I’m Hammad. I write for this website to help you with the IT advice about PC, RAM, CPU, Motherboard, PSU, and other PC components.
I will provide detailed guides with images, and explain step by step so you can understand the process. Check all my articles here.