Laptop SSDs use a fraction of HDDs’ power, leading to greater efficiency and extended battery life.
Hard disc drives (HDDs) are the standard data storage device, and they read and write data using spinning platters. SSDs are advanced storage devices that store data on memory chips, allowing immediate access. SSDs and HDDs have advantages; SSDs are more durable, quieter, faster, smaller, and use less energy, while HDDs have more storage space and are easier to recover data if damaged.
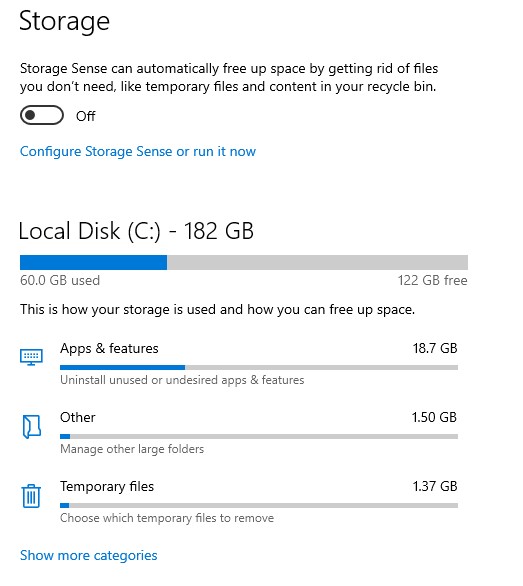
If you want to upgrade your company’s storage facilities, keep reading! Consider upgrading or adding some if you need more storage space. In any case, you’ve found the appropriate place. To help you decide which storage discs are best for your company, we’ve compiled this technical breakdown of SSDs vs. HDDs and how much power SSD and HDDs consume on average.
How Much Power Does SSD & HDD Consume in A Laptop on Average?
Solid-state drives (SSDs) consume less power than hard disc drives (HDDs); they don’t have any moving parts. Compared to the HDD’s power consumption of 6–15 Watts, the SSD’s consumption is merely 2–5 Watts. HDDs in servers consume 7% of the power, while SSD consumes 1% of energy.
Since solid-state drives (SSDs) don’t become as hot as hard disc drives (HDDs), they use less energy when running fans. SSDs are usually idle, so they consume less power than HDDs, which must spin constantly to read and write data.
There is no comparison between SSD and HDD performance. Modern solid-state drives (SSDs) have read rates of up to 550MBps and write speeds of up to 520MBps for sequential data. Hard disc drives can only read and write sequential data at speeds of up to 125 MB per second. There are distinctive differences between the both.
Both solid-state drives and hard disc drives (HDDs) store data, although they do so in very different ways. When it comes to storing and retrieving data, SSDs, and HDDs couldn’t be more different. HDDs rely on mechanical spinning discs and a revolving read/write head when accessing data, while SSDs rely on memory chips. Modern SSDs are as reliable as HDDs, making them the superior choice if cost is no object.
Power and Efficiency of SSD and HDD
The former wins in speed when comparing solid-state drives to hard disc drives. Standard SATA SSDs can copy 500 MB per second, but HDDs can only copy 30 to 150 MB per second when transferring large files. Modern NVMe SSDs reach incredible speeds of up to 3,500 MB/s.
While it would take a hard drive at least two minutes to replicate a 20 GB movie, an SSD can do it in under 10 seconds. Any computer, Mac or PC, will benefit greatly from having an SSD installed or upgraded.
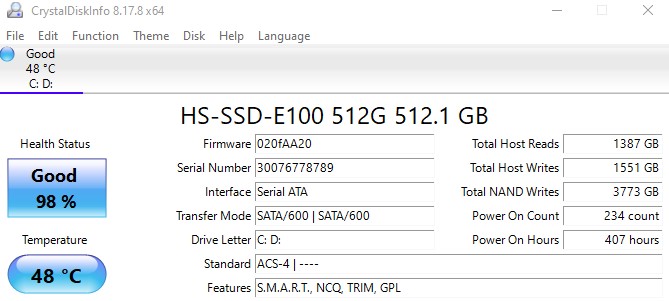
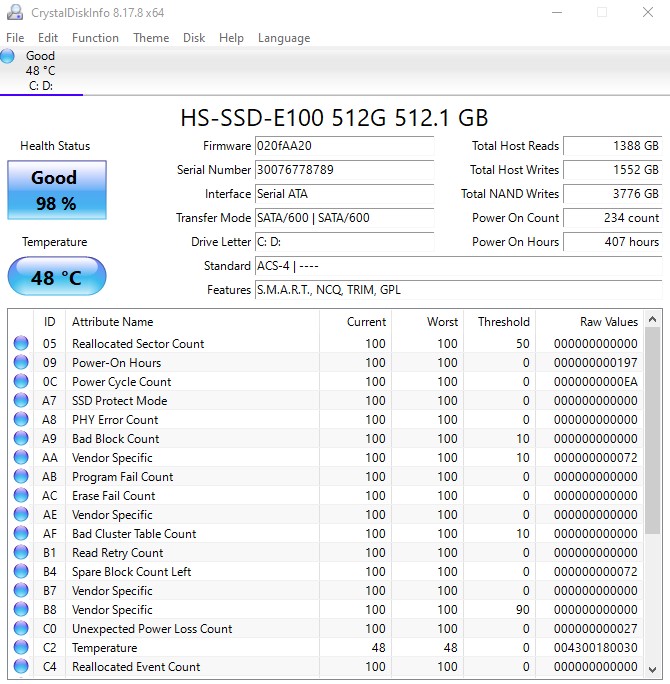
That’s how much quicker a solid-state drive is than a hard disc drive. An SSD is the quickest way to load huge amounts of data, such as a video file you’re editing. One of the main benefits of solid-state drives (SSDs) over hard disc drives (HDDs) is their faster read/write times. You can utilize software like CrystalDiskInfo to check the details of your HDD or SSD.
HDD and SSD Power Consumption
HDDs use a metal disc that spins at high speed and a component called a head to read and write data, so the motor uses a lot of energy. Laptop computers often employ the narrower 2.5-inch variety of the internal HDD, while 3.5-inch HDDs are also available. Power consumption is independent of drive capacity, contrary to common belief.
If they are the same manufacturer and production line, a 500 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB, 4 TB, or 6 TB HDD will all need the same power. The speed of the platter or disc has the greatest impact on this metric. Increasing the power consumption involves turning the recording disc rapidly to enhance the read/write speed. HDDs are more power-hungry than SSDs since they employ mechanical parts and a spinning platter.
There are no moving parts in an SSD, and thus uses far less power than a hard disc drive (HDD). Since the power consumption of an SSD is substantially lower, you shouldn’t compare it to the specifications of a traditional hard drive. During recording, the power consumption of solid-state drives (SSDs) connected through a SATA revision 1, 2, or 3 interface does not exceed 3.5 watts and averages 2 watts.
Such a device uses 0.5 watts of power when doing nothing and only 0.05 to 0.1 watts when sleeping. M.2 drives have a similar design to SATA storage devices. However, they connect to the computer via a separate slot. As a result, the power consumption of M.2 discs is equivalent to that of 2.5-inch SATA drives.
Capacity Differences
If you’re worried about how much data can fit on each disc type, rest assured. No distinctions in stowage size exist. HDDs and SSDs are available in capacities ranging from 128 GB to 20 TB and beyond. However, the price per gigabyte is a major differentiator between HDDs and SSDs. Thus, the latter will be significantly more expensive. The cost difference between hard drives and SSDs is significant.
Meanwhile, formatting any internal or external hard drive, HDD or SSD, is a simple process that greatly increases available storage space. There are methods available to delete everything from your hard drive. The more you store on the same drive, the messier it will get. You have a lot of programs on your computer that are constantly making temporary files in addition to the games, videos, and images you continually upload.
Durability Period of SSD or HDD
The science behind SSDs is rapidly developing. Solid State Drives had far shorter lifespans and fewer write cycles a few years ago. However, modern SSDs can withstand normal use for up to 10 years. Hard drives now have a consistent 5- to 10-year lifespan.
Due to the lack of moving parts, the absence of heat, and the resistance to shock and magnetic interference, SSDs outlast HDDs. Modern SSDs also provide increased reliability and longevity for your data. Hard disc drives (HDDs) have an annual failure rate of 2-5%, whereas solid-state drives (SSDs) are about 0.5%.
SSDs’ limited read and write cycles are one of their disadvantages. It implies that even with proper maintenance, SSDs will eventually require replacement. A typical solid-state drive (SSD) has a maximum write cycle of around 3000 before the disc cells start to degrade.
Which Storage Device is Best for Laptop: SSD Or HDD?
SSD is ideal for laptops because of its high speed, low energy usage, and long lifespan. It makes the system start-up and application load times faster. While HDDs give greater capacity at a lower cost, SSDs provide a considerable performance gain, making them suitable for a better user experience.
Most laptops and portable devices utilize SSDs. It is because they are not moving parts. The longer battery life directly results from the lower power consumption of solid-state drives. Most recent laptops in the medium and upper price ranges have SSDs. However, cheaper models may still have HDDs. Unlike hard discs, solid-state drives don’t experience any damage from being dropped.
If you decline it while the read/write head moves, it can corrupt data on a laptop hard drive. SSDs prevent this from happening. But there is only sometimes a binary option to pick from. In a “hybrid” computer, the SSD contains the operating system (OS), applications, and commonly used files, while the HDD stores all other data.
In a “hybrid” computer, the SSD contains the operating system (OS), applications, and commonly used files, while the HDD stores all other data., which is larger and less expensive. Using an SSD to run the operating system and applications in a hybrid configuration is a fantastic approach to boosting SSD performance.
Does an SSD Use Less Energy Than HDD?
SSDs often have slightly higher power requirements than HDDs. That may come as a shock to you. Everyone knows that HDDs need a motor to spin up their discs. However, most SSDs will still use significantly more energy than HDDs. SSDs’ design makes them more data-intensive than HDDs.
Solid-state drives contain several chips and other electronic parts. Therefore, even if you only need to store 1MB of data, most chips must be engaged, necessitating some power. The power consumption occurs only when the HDD’s disc needs to revolve. When there is no task to perform, the disc will stop spinning, and the motor will come to a rest. While working on RAM-intensive tasks, this can continue for much longer.
However, solid-state drives require additional information for purposes like wear-leveling and data storage. In actuality, solid-state drives (SSDs) store data electronically. Starting an SSD consumes more power than a traditional hard drive because it requires capacitor charging. In addition, the SSDs will only spend a little time sitting idle.
Which Is Faster, An SSD Or an HDD?
SSDs are much quicker than HDDs. SSDs store their data in flash memory, allowing them to access it instantly without needing moving parts. As a result, the system is more responsive and boots up in less time than a standard HDD, which uses spinning disks and moving elements.
Creators developed newer technologies like solid-state drives (SSDs) to address HDD weaknesses, particularly speed and performance. Access times to data on solid-state drives are less than 0.1 microseconds. Hard drives take 5.5 to 8 ms. SSDs have improved in speed, stability, and reliability. When comparing read/write speeds, the SSD is superior to the HDD.
The input/output data request time for hard disc drives is 400–500 microseconds, while that for solid-state drives is just 10–20 microseconds. In terms of speed, SSDs are more than one hundred times as fast as HDDs. SSDs can read and write over 6,000 times a second, while HDDs can only manage 400 operations on average. As a result, applications launched from the SSD will operate and store data more quickly than those found from the HDD.
Tips for Optimizing Power Consumption
You can utilize the power-saving features of your system, utilize an SSD over an HDD, use an external hard drive to get more room for data, keep a check over background applications and processes, optimize the startup programs, and keep your software up-to-date.
To get the most out of your laptop’s battery life, especially while you’re on the go or in a position with limited access to power, it’s important to optimize its power consumption. You may save electricity and use your laptop’s battery more if you follow some simple guidelines.
This section includes in-depth advice on reducing power consumption across a wide range of factors, including hardware, software settings, and individual behaviors. These tricks will help you maximize your laptop’s battery life, whether you’re a regular traveler or just looking for ways to boost your computer’s performance.
- Utilize Power-Saving Features
Utilize the battery-conserving options provided by your laptop’s OS. Controls for power management of the central processing unit (CPU), display, and other peripherals may be included in this category. Reduce your energy bill by activating and tweaking these options to your liking.
- Use an SSD over an HDD
Compared to conventional Hard Disc Drives (HDDs), the power requirements of Solid State Drives (SSDs) are significantly lower. Investing in a solid-state drive (SSD) is a good idea because it will improve your device’s performance and battery life.
- Utilize an External Hard Drive
Choose an external hard drive if you need more room for your data. Remember, though, that external discs will drain your laptop’s battery. If you’re trying to save some juice, only plug in your external hard drive when necessary.
- Keep a Check on Background Processes
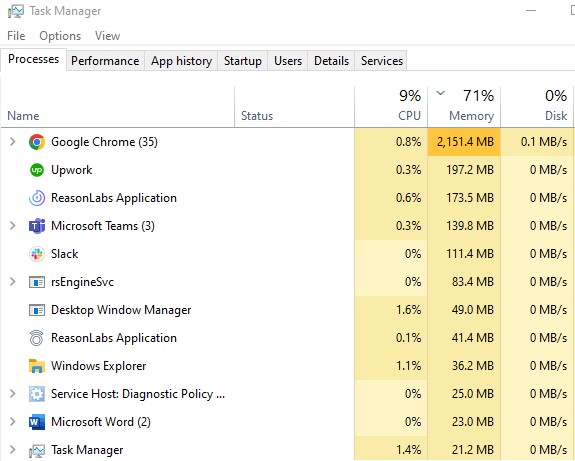
Stop any running programs in the background that aren’t necessary. Many apps operate in the background, eating up battery life even when you’re not using them. Reduce your computer’s energy consumption by closing unnecessary programs using the Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac).
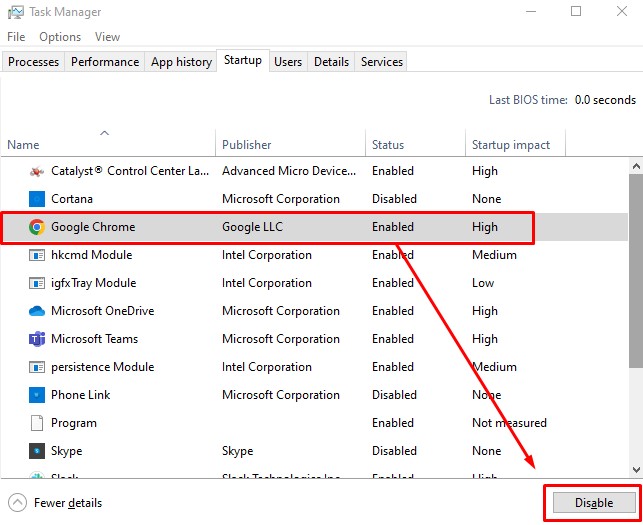
- Optimize the Startup Programs
Take a look at the software that starts up on your laptop. To speed up the boot process and save energy, it is recommended that any unused programs in the starting list be disabled. Task Manager (Windows) and System Preferences (Mac) allow you to manage which applications launch when the operating system boots.
- Keep Software Up-to-date
Make sure your software and operating system are always up to date. Power optimizations and bug patches are common components of software updates, which can improve efficiency. It’s important to regularly check for updates and implement them to reap the benefits of these enhancements.
- Lower the Use of USB Device
Using several USB devices simultaneously, your laptop’s battery may drain faster. Disconnect unused USB devices and keep the number of linked devices to a minimum. It lowers energy needs and lengthens battery life.
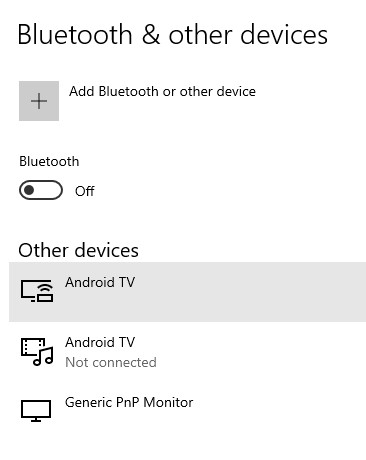
- Adjust Wireless Connectivity Power Settings
Even when not in use, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connections drain the battery. Optimize your use of these wireless functions by adjusting their power settings. For instance, you can put your Wi-Fi or Bluetooth into hibernation or sleep mode while they’re not in use.
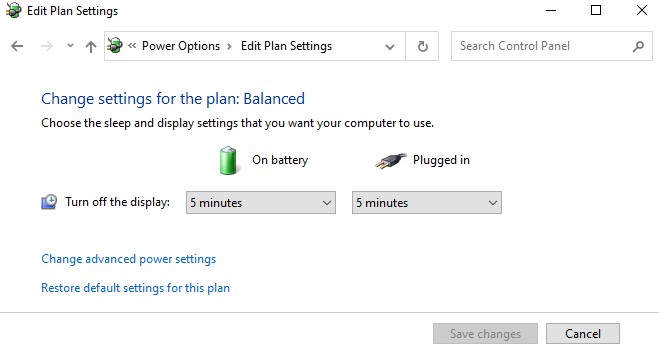
- Lessen the Screen Timeout
Reduce the length of time the screen stays on before going to sleep. It implies the screen will go dark after less inactivity, which is good for saving energy. You may change the screen timeout by going into your device’s power or display settings.
- Use Extensions that are Power-Efficient
Power consumption can be lowered by using specific browser extensions. Keep an eye out for add-ons that claim to reduce power consumption or increase battery life. These add-ons are useful for managing resource-heavy websites and decreasing background processes, advertisements, and content.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when choosing laptop storage devices, the power consumption of SSDs and HDDs is important. SSDs use less electricity than HDDs since they have no moving parts. SSDs need 2–5 watts, and HDDs 6–15. Solid state drives lack spinning discs, and read/write heads make them power efficient. SSDs provide benefits beyond power consumption.
They improve performance, durability, and access speeds. Solid state drives beat HDDs, which normally transmit data at 125 MB per second, with read and write speeds of 550MBps and 520MBps, respectively. SSDs excel in system startup, file transfers, and data-intensive applications. SSDs are compact, silent, and shock- and drop-resistant.
Power efficiency and endurance make them ideal for laptops and portable devices. Modern SSDs can live up to 10 years under normal use compared to HDDs. In addition to considering the advantages of SSDs, it is essential to consider the restrictions imposed by SSDs. They cost more than HDDs, especially for larger capacities. Despite falling SSD prices, HDDs are still cheaper for storing big data. SSDs have limited write cycles.
HDDs offer cheaper, bigger storage capabilities. They are long-term storage and interface-compatible. HDDs are mechanical. Therefore, they’re slower and more likely to break. Hence SSDs and HDDs differ in affordability, performance, storage capacity, and use cases. SSDs are great for laptops and applications that need speed, power efficiency, and durability. HDDs are cheaper and more compatible for huge data storage. Individuals and companies must thoroughly examine their demands to find the best storage option.

Hey, I’m Hammad. I write for this website to help you with the IT advice about PC, RAM, CPU, Motherboard, PSU, and other PC components.
I will provide detailed guides with images, and explain step by step so you can understand the process. Check all my articles here.