Have you ever thought of an ideal loudness of the PC? Want some tips on how loud should your PC be? Let’s delve into the facts and figures.
The noise level of a PC is a crucial aspect to consider when building or using a computer system. It refers to the sound produced by components, such as cooling fans, power supply, and hard drives.
The usage and workload of the PC also play a role, with idle situations typically requiring a minimal noise level and heavy load scenarios potentially increasing the noise output. Striking the right balance between noise and performance is key, considering personal preferences and the environment in which the PC is used. This post will elaborate on how loud a PC should be, the factors affecting the loudness, and the measures to control the loudness.
How Loud Should My PC Be?
A gaming PC ideally produces noise levels below 35 decibels (dB) during low-load situations and 45 dB under heavy load. In contrast, a normal PC generates noise below 30 and 40 dB during low and high-load activities. Thus, PC (including gaming and normal PCs) noise levels vary on personal preferences.
DB, or decibel, is a unit used to measure the intensity or level of sound and the ratio between two levels of power or amplitude. Each increase of 10 dB represents a tenfold increase in sound intensity. For example, a sound 10 dB louder than another sound is perceived as being twice as loud.
As a computing geek, you must know the importance of quiet PC components. It is not just important to avoid noise. A louder PC impacts your overall user experience and makes the surroundings uncomfortable for any other task. Let’s unveil other drawbacks of a loud PC:
- Distraction
A loud PC can be distracting, especially in quiet environments or during tasks that require concentration. The constant noise generated by fans or other components can disrupt your focus and hinder productivity.
- Discomfort
It is difficult to carry out any task on a noise-generating PC or in its surroundings. Prolonged exposure to loud noise levels causes discomfort and irritation. It may lead to headaches, increased stress levels, and a generally unpleasant computing experience.
- Communication Interference
If you use voice communication tools, such as online meetings, streaming, or gaming, a loud PC can interfere with clear communication. The noise is picked up by your microphone and transmitted to others, causing difficulty in understanding or hearing you properly.
- Component Lifespan
The PC noise is generated through any PC component. So, constant exposure to high noise levels can potentially impact the lifespan of certain PC components. For instance, vibrations and excessive heat contribute to wear and tear on components like fans, causing them to fail prematurely.
Ultimately, a loud PC negatively impacts the overall user experience. It is experienced and quoted that excessive noise detracts you whether you use your PC for work, entertainment, or everyday tasks. Keeping in view, the upcoming section of this post intends to highlight the possible measures to control/minimize the loudness of the PC.
How to Determine an Ideal Loudness Level for My PC?
The ideal noise level for a PC varies based on individual preferences. Some users are sensitive to noise and prefer whisper-quiet systems, while others can compromise in such a situation. It’s crucial to consider your comfort level and the noise level you find acceptable during computer use.
- Noise Sensitivity
Factors like the environment in which the PC is located can influence how noise is perceived. Quieter environments, such as a home or office, require lower noise levels to avoid distractions, while in a louder environment, like a gaming arena, slightly higher noise levels might be more tolerable.
- Distractions and Comfort
Excessive noise can be distracting and impact concentration. For tasks requiring focus, such as content creation or studying a quieter PC can enhance productivity and comfort. On the other hand, in a casual setting, such as a living room, a slightly higher noise level may be more acceptable.
- Gaming and Performance-Intensive Tasks
Some users prioritize maximizing PC performance over noise reduction during gaming or other performance-intensive tasks. This trade-off increases noise levels due to increased fan speeds or more demanding components. Finding a balance that meets performance needs while minimizing noise is key.
How to Control the Loudness?
When it comes to PC noise levels, components such as fans, hard drives, dust factor, etc., play a significant role in determining the overall noise output. Understanding these components can help identify potential noise sources and find ways to mitigate them.
By learning the factors and the measures to control them, you can maintain the balance between the performance and the noise, which is the ideal situation where the loudness is in control.
Cooling Fans
Cooling fans are essential for maintaining optimal temperatures within the computer system. However, they can be a significant source of noise. The number, size, and quality of fans impact the noise level. Fans with higher RPM (revolutions per minute) tend to generate more noise.
To rectify this, you must choose high-quality fans designed for low-noise operation. For this, look for models with features like larger blades, fluid dynamic bearings, or noise-reducing technologies. Let us list some characteristics of the fans that are best recommended for noise reduction:
- Larger Fan Size
Larger fans tend to move more air at lower speeds, which reduces noise compared to smaller fans running at higher speeds. For example, a 120mm fan can operate around 25 dB, while an 80mm fan might generate noise at 35 dB or higher.
- Lower RPM (Revolutions Per Minute)
RPM is the factor that determines how fast the blades move in one minute. It is also the primary factor affecting the fan’s performance. Fans with lower RPM ratings generally produce less noise. Thus, look for fans designed for low-noise operation or those labeled as quiet or silent fans.
- Advanced Bearing Types
Fans with advanced bearing types, such as fluid dynamic bearings (FDB) or magnetic levitation (maglev) bearings, tend to offer smoother and quieter operations than traditional sleeve or ball bearings.
- Fan Blade Design
The design of the fan blades determines the overall noise produced by the fans. The curved or angled blades help optimize airflow and reduce noise generation. So, it would be best to get the fan with curved and angled blades, not the straighter ones.
- Anti-Vibrant Mounts
What if you are feeling a vibration that is producing noise? In such a case, you must try anti-vibrant mounts or rubberized frames. These components help in reducing the vibration, ultimately reducing the noise transmission.
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Control
In the context of fan control, PWM control adjusts the fan speed by varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal. The duty cycle represents the on-time ratio to the PWM cycle’s total time. Adjusting the duty cycle can increase or decrease the fan’s speed.
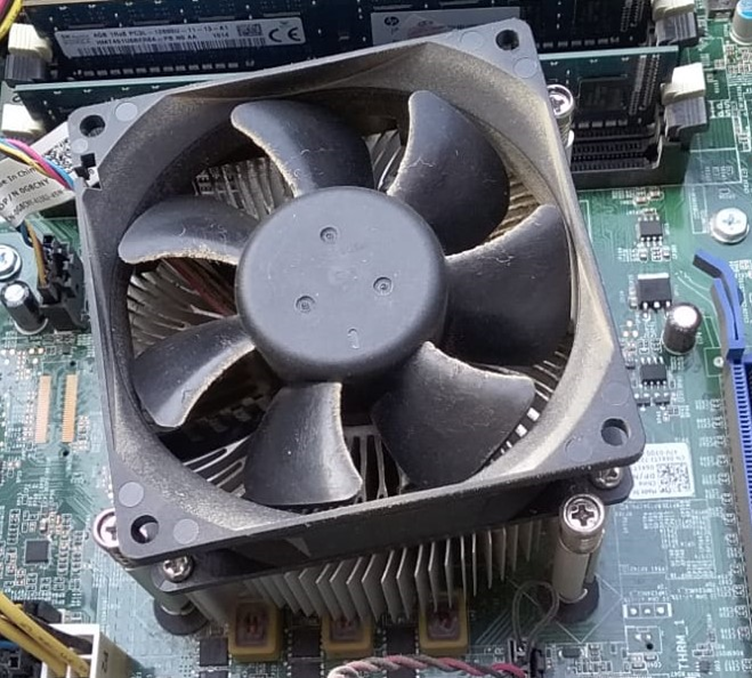
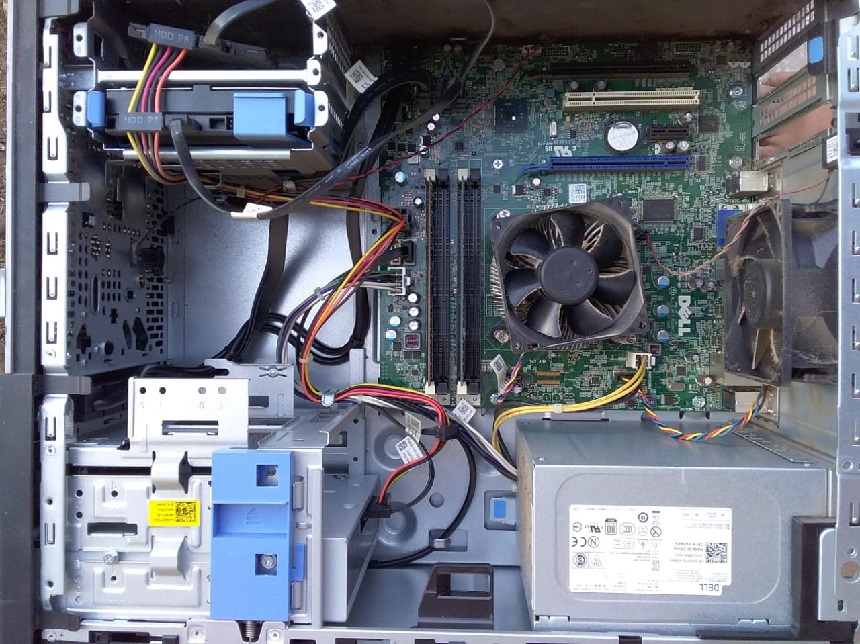
Multiple fans on the PC are supposed to control the temperature of the specific component. For instance, the image provided below illustrate the fan(s) that normalizes the CPU temperature:
Similarly, the fan (in the image below) at the upper part controls the temperature of the PSU, while the fan at the lower half is supposed to cool down the overall temperature of the CPU case (refers to all the components):
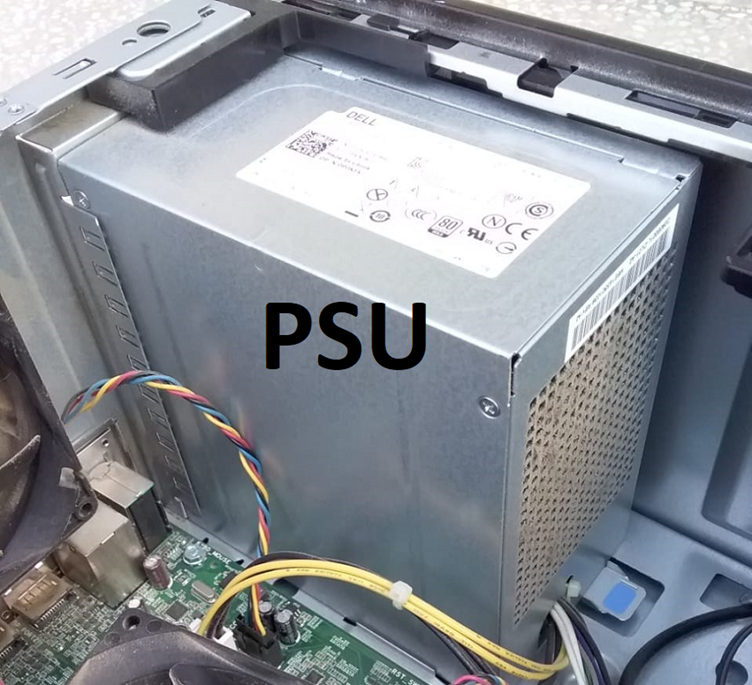
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
PSU converts AC power from the electrical outlet into DC power for the PC’s internal components. Modern PSUs are generally quieter and cheaper, whereas older models generate more noise. The higher-wattage power supplies tend to have larger fans, which can contribute to increased noise.
The Power Supply Unit is the primary component that connects your hardware components with the power-providing source, i.e., electricity majority. It is recommended to attain the best PSU. Do you need clarification while choosing PSU? Let’s guide you on what components to consider while purchasing PSU.
- Power Requirements
To choose the best PSU, you need to determine the power requirements of your system by calculating the total wattage needed for all components. While selecting the PSU, ensure the PSU has sufficient wattage to accommodate the system’s needs, with some room for future upgrades as well.
- Modular/Non-Modular Design
Modular PSUs allow you to detach unused cables, reducing cable clutter and improving airflow. Non-modular PSUs have all cables permanently attached. While choosing Modular/Non-Modular designs, you must consider your cable management preferences and the case design.
- Quality and Reliability
The overall quality and reliability of the PSU depend on the manufacturer or the standards used during manufacturing. You can read reviews and even check for certificates, i.e., UL, TUV, or CE. The reviews and certificates ensure the PSU meets safety and performance standards.
- Fan Noise and Cooling
One of the major components in the PSU is the fan mounted inside it. Choose a PSU with fans specifically designed for quiet operation. Some PSUs have semi-passive or zero RPM fan modes, where the fan remains off or spins at low speeds during low load conditions. Additionally, consider the PSU’s cooling capabilities to ensure efficient heat dissipation.
- Connector/Cable Length
The connecting cable must be good enough to get the ideal performance of the PSU. The selected cable must be compatible with the system components, i.e., quality, length, wattage transmission, etc.
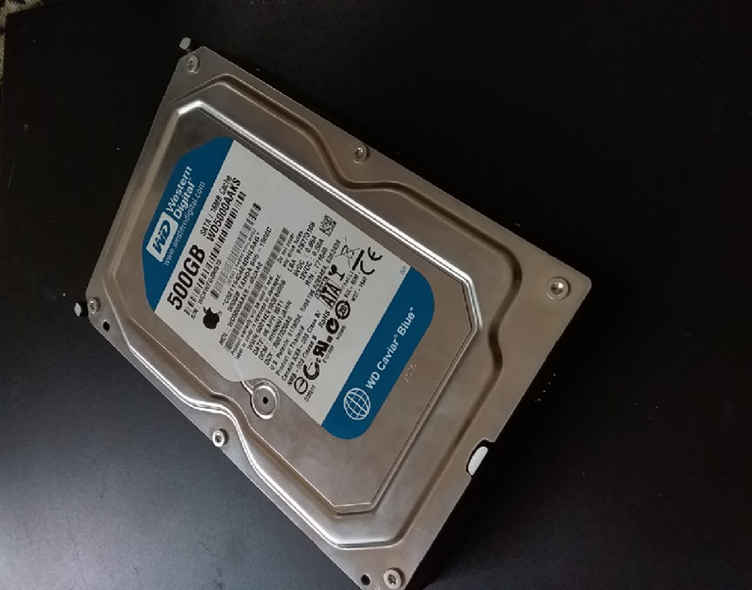
Hard Drive
Traditional/mechanical hard drives consist of spinning platters and moving read/write heads, which can produce noticeable noise during operation. Mechanical hard drives (HDD) have moving parts that create inevitable little noise. Moreover, if the HDD has turned older, its moving disk creates more sound than normal. The image of the mechanical HDD is attached below:
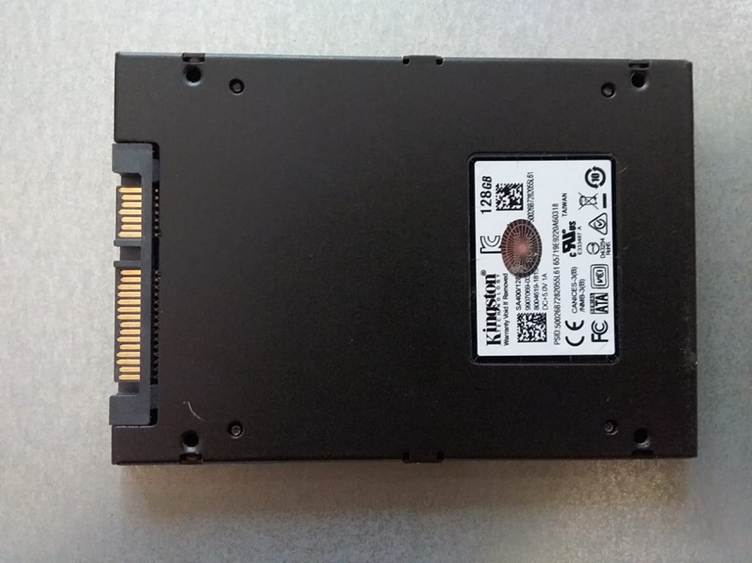
It is suggested to replace it with Solid State Drives (SSDs), modernized enough, and have no moving parts, resulting in lesser or no noise. Look at the image of the SSD attached below, i.e., it is compact, has no sound, and provides fast data transmission too.
Dust
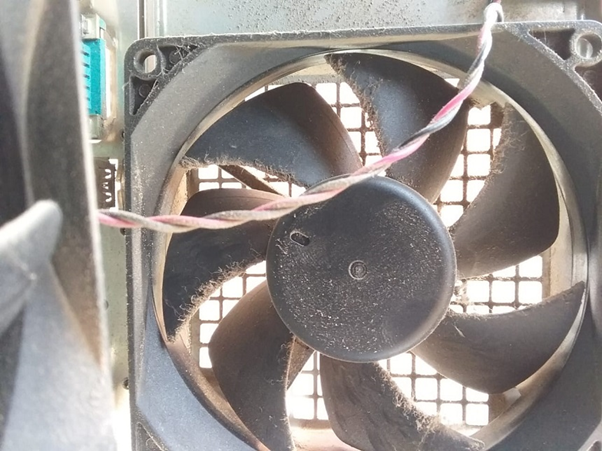
Dust is the leading environmental factor affecting the hardware components’ overall performance. In some cases, the CPU case is kept open to normalize the temperature, which can be a dust-catching factor. Look at the image attached below; the fan and its surroundings are overloaded with dust:
It is recommended to spare a few min regularly uses to clean up the dust from your PCs regularly. You can use compressed air or an antistatic brush to remove dust from fans, heatsinks, and vents.
Apart from the above-stated factors and their control measures, a few quick remedies need to be practiced to control the loudness of the PC. Let’s get into these:
Graphics Card
Graphics cards, especially high-performance models, often have fans to dissipate heat generated during demanding tasks like gaming or rendering. These fans can contribute to the overall noise level. Selecting graphics cards with efficient cooling solutions or utilizing fan speed control can help manage noise associated with the GPU.
Acoustic Foam and Padding
Acoustic foam and padding are usually used for soundproofing a specific area. These materials absorb noise and reduce propagation, resulting in a quieter environment. The foam/padding can be applied inside your CPU case to minimize or make the PC soundless.
Optimal Cooling
If your PC is heating up continuously, your fan may be noisy. So, adequate cooling is essential for reducing fan noise. You need to ensure airflow paths are clear and unobstructed. Also, verify that fans are working correctly and consider adding additional fans or upgrading cooling solutions if necessary.
Moreover, the environment in which the PC is being used also matters greatly. If the surroundings of your PC are at a higher temperature, then you have to change the place of your PC or get some equipment to normalize the surroundings, i.e., an air conditioner.
Are Gaming PCs Supposed to be Loud?
Gaming PCs are not necessarily supposed to be loud, but they can be louder compared to regular PCs due to their higher performance and cooling requirements. Gaming PCs often include powerful components, such as high-end graphics cards and processors, which generate more heat and require more robust cooling solutions.
With advancements in cooling technology and the availability of quieter components, it is possible to build gaming PCs that offer excellent performance while maintaining relatively low noise levels. Ultimately, the noise level of a gaming PC can vary based on factors like component selection, cooling solutions, and individual preferences for noise tolerance.
Wrap Up
The phrase “How Loud Should my PC be” is considered by each technology enthusiast, whether a gamer or a normal computer user. Experts recommend that the loudness of a gaming PC must range from 35 dB (min) to 45 dB (max) and 30 dB (min) to 40 dB (max) for the normal PC.
The loudness of the PC depends on various factors, such as the cooling fans, their blade/overall size, and the fan’s RPM. The PSU is also one of the factors to consider alongside the graphics card (if applicable). Each hardware component must be optimized to balance the performance and the noise.
If you are a gaming enthusiast, you must ensure that the cooling fans fulfill all the necessities; the blades are larger, well-shaped, and have low RPM. You also need to ensure that you use Solid State Drives as the storage medium. For better performance, try using anti-vibrant mounts to nullify the vibrations.
All in all, the loudness depends on your preferences or the hardware components you use. You must optimize the PC components discussed in this guide or prepare yourself for a noisy PC.
In the end, you have now learned about “How Loud Should my PC be?“, the factors affecting the loudness, and how to control the loudness of your PC.

Hey, I’m Hammad. I write for this website to help you with the IT advice about PC, RAM, CPU, Motherboard, PSU, and other PC components.
I will provide detailed guides with images, and explain step by step so you can understand the process. Check all my articles here.