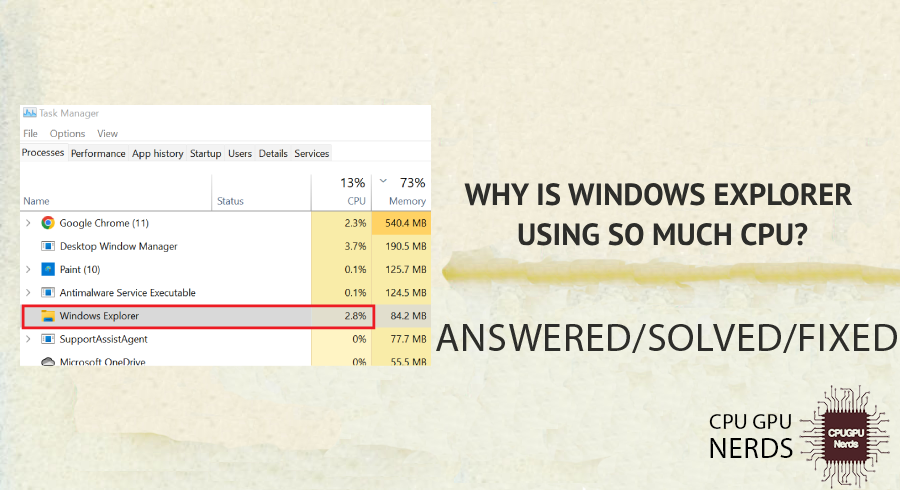
Windows Explorer, also known as File Explorer, is part of the Microsoft Windows operating system that serves as the primary file management tool for millions of people around the world. It enables you to easily navigate, organize, and access your files and folders.
However, Windows Explorer’s high CPU utilization can have a negative impact on other running apps, causing them to respond slowly or freeze. This causes delays and potential frustration for users. Addressing this concern ensures a seamless and efficient experience while managing files and folders with Windows Explorer’s extensive capabilities. Users can maximize productivity and enjoy a smoother computing experience by optimizing its performance.
In this article, we will look at the most prevalent causes of excessive CPU consumption in Windows Explorer and give solutions to resolve the problem. You’ll learn how to disable specific features, delete temporary files, and dig for potential sources of the problem. By following these suggestions, you may not only fix the present problem but also optimize the long-term functionality of your system.
Why is Windows Explorer Using so Much CPU?
This can be attributed to the extensive indexing of files and folders, which strains system resources. Another contributor is third-party extensions that may not be optimized, overburdening CPU usage. Both system-related, and user-specific behaviors play a role in these resource demands.
Also, it might slow down your system, interfere with multitasking, and even cause unresponsive behavior. Several factors, including the following, could cause this issue:
- Quick Search Indexing
If you have many files or a complex folder structure, indexing can use a substantial amount of CPU, particularly during initial setup or after significant file modifications. In Windows Explorer, search indexing entails continuously scanning and cataloging files and directories on your system to generate an index database providing speedy search results. - Third-party Shell Extensions
Shell extensions are third-party add-ons that interface with Windows Explorer for additional functionality. But poorly designed or outdated shell extensions, on the other hand, can cause conflicts. These extensions are invoked when you access or interact with files or folders. If they are inefficient or have problems, they can waste significant CPU resources, slowing down Windows Explorer. - Malware or Virus Infection
Malicious software can lurk within Windows Explorer processes and use CPU resources to perform unauthorized actions. Furthermore, certain malware strains are engineered to elude detection by security software and function discreetly within normal operations, making user identification difficult. A high CPU use by an infected Windows Explorer process frequently indicates an underlying malware problem that demands rapid care. - Corrupted System Files
Corrupted system files might cause problems by producing strange behavior in Windows Explorer. Various circumstances, including power outages, hardware problems, and software incompatibilities, can cause corrosion. When Windows Explorer tries to access or process faulty files, it may enter a loop of repeated attempts, leading the CPU to work on the same task indefinitely. - Large Media Files
Windows Explorer may consume additional CPU resources when handling large media files, such as high-resolution photographs or videos. Also, some media files contain substantial metadata, such as EXIF data in photos or video tags. Windows Explorer reads and processes this metadata to display relevant information in file properties or metadata columns, contributing to the problem. - Thumbnail Generation For Files
Creating thumbnails for huge media files can be computationally demanding, resulting in higher CPU utilization. When you open a folder containing huge media files, Windows Explorer tries to build thumbnails for each file so that you may see a glimpse of it. - File and Folder Operations
File and folder activities, such as copying, moving, or deleting a large number of files, can significantly increase the CPU utilization of Windows Explorer. When you do these tasks, Windows Explorer must process each file separately, which can be time-consuming.
Furthermore, copying or moving many files necessitates reading and writing data, which can burden the CPU if the files are large or spread across multiple storage locations. Similarly, deleting many files requires Windows Explorer to update the file system and remove references to the removed files, both of which can be CPU-intensive. - Resource-Intensive Tasks
Background resource-intensive operations might cause Windows Explorer to consume substantial resources. Other apps or processes that need a considerable portion of the CPU’s processing capacity can be included among these tasks.
Handling huge files or directories is a common resource-intensive operation. When users interact with large media files, high-resolution photos, or sophisticated documents in the Explorer window, Windows Explorer requires more processing resources to display them in the Explorer window. - Outdated Operating System or Driver
An outdated operating system or drivers can cause incompatibility difficulties with Windows Explorer. Drivers are used to ease interactions between Windows Explorer and the operating system or hardware components.
If the drivers are outdated or incompatible with the current operating system version, inefficiencies, errors, or crashes might occur, consuming additional CPU resources. This can lead to slower response times, slower file operations, and increased CPU utilization by Windows Explorer when attempting to conduct tasks. - Conflicts Due to Resources
Resource conflicts can occur when numerous software programs or processes compete for the same system resources, such as CPU time, memory, or disc access. When Windows Explorer faces resource conflicts, it may experience delays or inefficiencies in completing operations, increasing CPU utilization.
How to Fix Windows Explorer Using So Much CPU?
To fix CPU-related issues, you can utilize a built-in Troubleshooter. Troubleshooting involves running diagnostic tools to identify and fix underlying issues causing high CPU usage. Cleaning File Explorer history entails clearing records of past activities, potentially alleviating CPU strain.
You can fix CPU issues by running a Troubleshooter, cleaning File Explorer history, and turning off search indexing. A clean boot, evaluating disc health, removing temporary files, enabling paging, and, if necessary, considering a Windows update or system restore can all help to optimize CPU consumption.
Moreover, remember to restart your computer after making adjustments to see if there is any improvement. If the issue persists, seek help from a skilled technician or a support forum to identify and resolve any underlying problems. Follow these methods to resolve Windows Explorer’s excessive CPU usage.
Disable Thumbnails for Files and Folders
To disable file thumbnails, go to the folder option in your file explorer. After disabling file thumbnails, Windows Explorer will no longer generate previews for files and folders, increasing efficiency on systems with low CPU resources or dealing with directories containing huge media files.
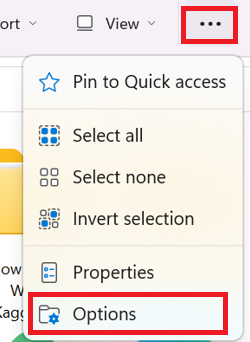
- First, open File Explorer by pressing the “Windows key + E” combination. Select “Options” from the toolbar after clicking the three dots in the top menu. Then, in the resulting “Folder Options” window, select the “View” tab.
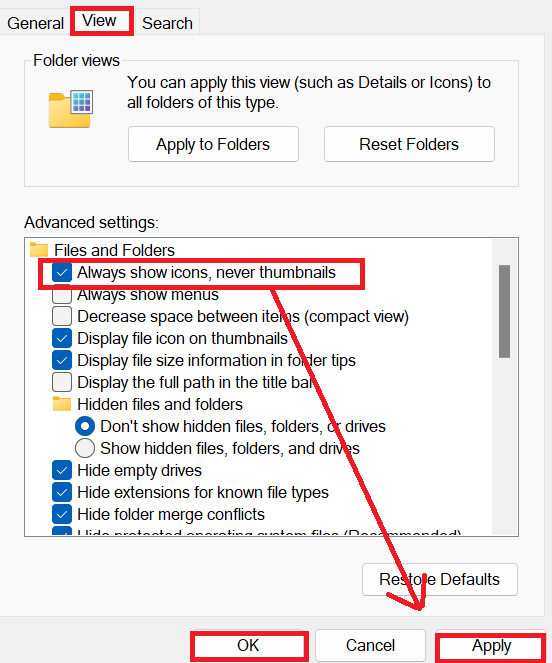
- Now locate “Always show icons, never thumbnails” under the “Files and Folders” section and check the box next to it. At the bottom of the window, click the “Apply” button, then click on “OK” to save the changes and dismiss the “Folder Options” window.
Disable Recently Opened Items in File Explorer
If you disable recently opened objects in File Explorer, Windows will no longer track and display your recently viewed files in the Quick Access section. This can assist in minimizing CPU consumption in Windows Explorer because it won’t have to maintain and update the list of recent items constantly.
- Firstly, press the “Windows key + E” combination to open File Explorer. Select “Options” from the toolbar after clicking the 3 dots in the top menu. Navigate to the “General” tab in the “Folder Options” window that displays.
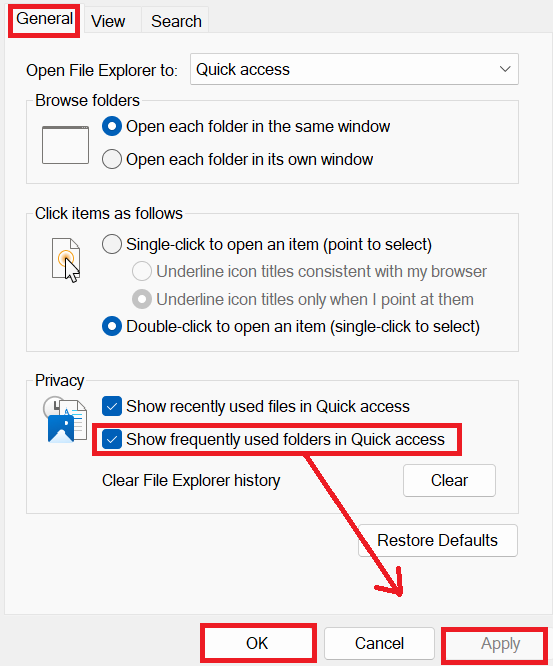
- Afterward, there is a setting under “Privacy” named “Show recently used files in Quick access.” Uncheck the box to the right of it. At the bottom of the window, click on the “Apply” button, then “OK” to save the changes and dismiss the “Folder Options” window.
Reset File Explorer and Enable Paging File
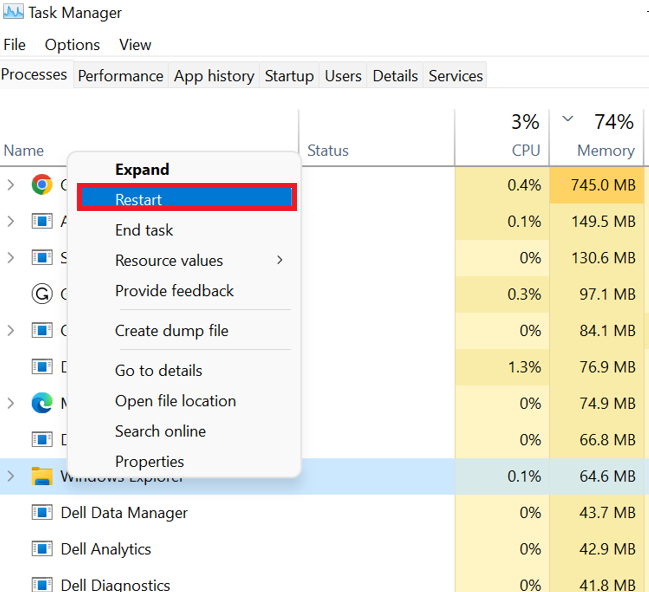
To reset the file explorer process, go to Task Manager, which gives it a fresh start and can fix any temporary issues, and then enable the paging file, which allows Windows to use a piece of your hard drive as additional memory, improving system performance.
- To restart the file explorer process, launch the Task Manager by pressing “Ctrl + Shift + Esc.” Navigate to the “Processes” or “Details” tab and look for “Windows Explorer” in the list of processes. Right-click “Windows Explorer” and choose “Restart” from the context menu. This will kill and restart the File Explorer process.
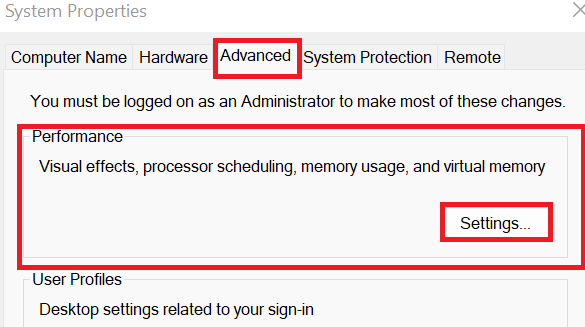
- Additionally, to activate paging files (Virtual Memory), you must open the System window by pressing the “Windows key + Pause/Break” combination. Then click on the “Advanced system settings” on the left side of the System window. Go to the “Advanced” tab in the System Properties box that displays. And click on the “Settings” button under the “Performance” section.
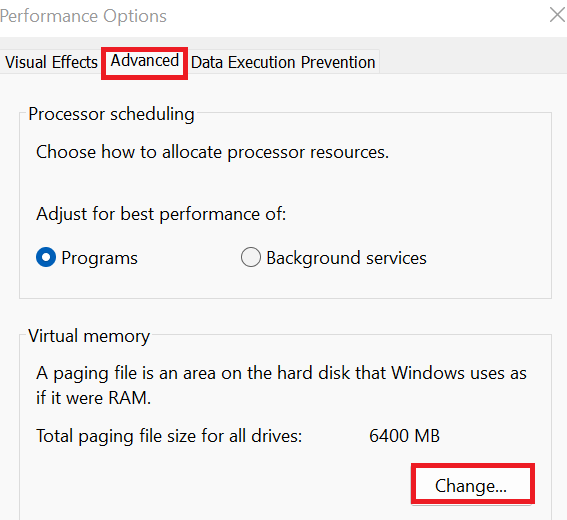
- Afterward, in the performance menu, go to the “Advanced” tab in the Performance Options box. Moreover, click “Change” in the “Virtual Memory” section.
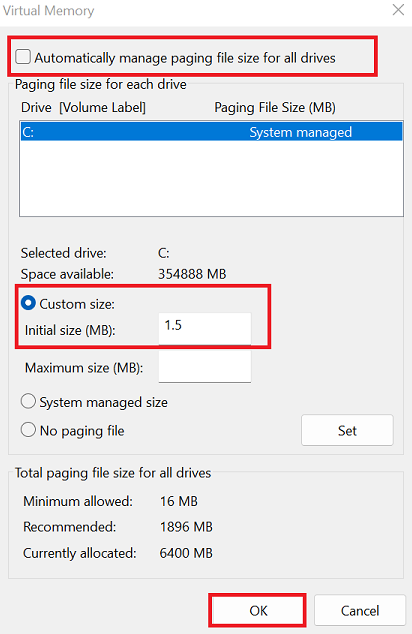
- Lastly, remove the tick mark next to “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.” Select “Custom size” and enter the same amount for the Initial size (MB) and Maximum size (MB), which should be 1.5 times your RAM size. Last, click “Set” and then “OK” to apply the changes.
Run SFC and Check Disk Scans
You can identify and repair any corrupted or missing system files and file system issues on your Disc by running SFC and Check Disc scans. Running these scans regularly as part of your system maintenance routine will help maintain your system stable and prevent future problems.
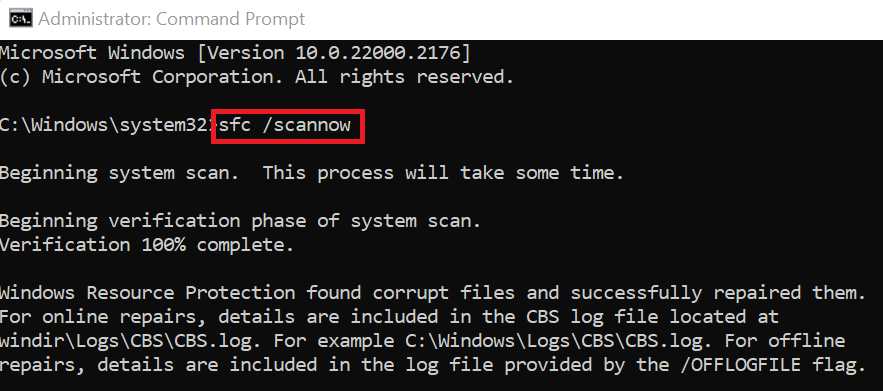
- To run SFC (System File Checker), open an elevated command prompt, use “Windows key + X,” and pick “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin).” Now enter “sfc /scannow” into the command prompt window and hit Enter.
- Hence the system file checker will search for corrupted or missing system files. This procedure could take some time. The tool will reveal the results once the scan is finished. If any problems are discovered, SFC will immediately attempt to rectify them.
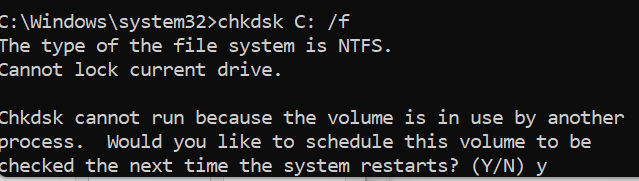
- Now to scan the Disc with Check Disc (CHKDSK), type “chkdsk /f” followed by the drive letter of the Disc you want to scan (e.g., C:) in the same elevated command prompt. Enter your password. When the machine restarts, you will be prompted to schedule the scan. Type “Y” and press Enter.
- After that, you have to restart your computer, and Check Disc will analyze your Disc for integrity, identify and repair any file system issues, and recover faulty sectors if necessary.
Perform System Scan
When malware or viruses enter a PC, they frequently run in the background, devouring CPU resources and rendering the system inoperable. You can detect and eliminate these risks by running a system scan using antivirus or security software, which can drastically reduce CPU utilization by Windows Explorer.
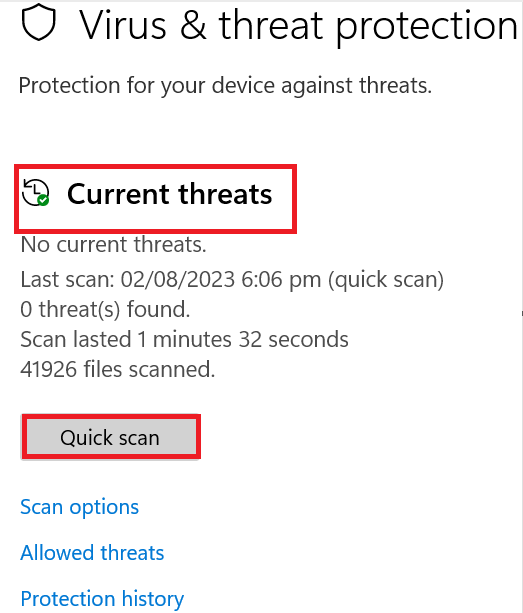
- Press the “Windows key + I” combination to open the Windows Settings app. Go to “Update & Security.” On the left sidebar, select “Windows Security.” In the Windows Security dialogue box, select “Virus & Threat Protection.”
- Now under “Current threats,” select “Scan options.” Choose “Quick scan” and press the “Scan now” button. Windows will briefly scan your system to look for potential threats.
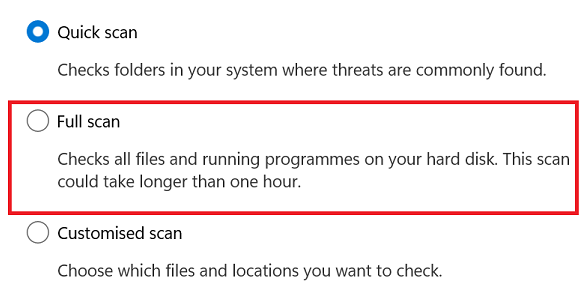
- Moreover, if the quick scan returns no results or you suspect a more severe problem, you can perform a comprehensive scan instead. Select “Full scan” in the “Scan options” window and click the “Scan now” button.
Depending on the size of your system and the number of files to be reviewed, the scanning procedure may take some time. Allow the scan to complete before continuing. When the scan is finished, you will see whether any threats were discovered. Follow the on-screen instructions to eliminate or quarantine any risks that are found.
Perform a Clean Boot
By executing a clean boot, you can prevent unneeded third-party programs and services from starting at startup. This assists in determining which of these applications or services is generating the high CPU consumption. It can help in determining the root cause of the main issue.
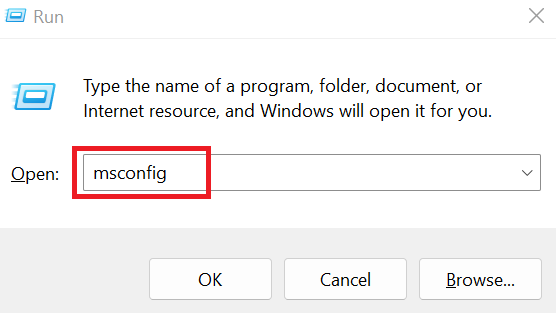
- To open your Run dialogue box, press on the “Windows key + R” combination. Then to open your System Configuration window, type “msconfig” and hit Enter. After that, navigate to the “Services” tab in the System Configuration window.
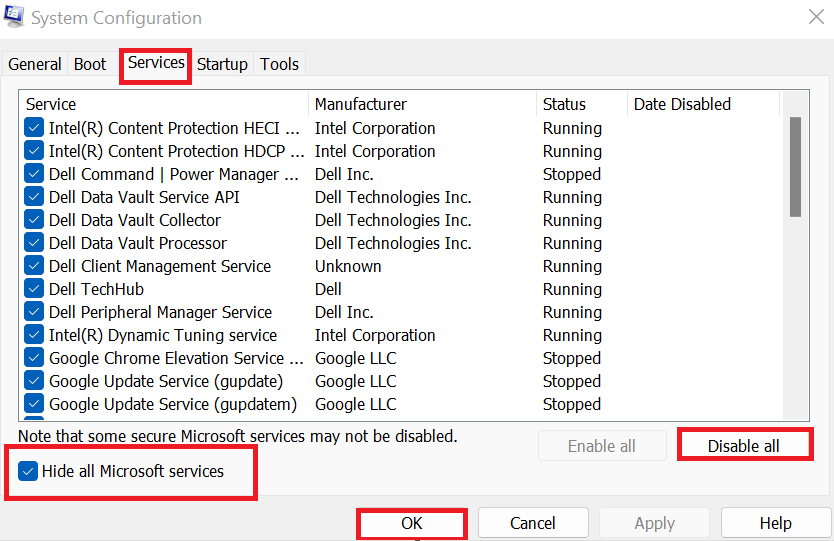
- Afterward, select the checkbox next to “Hide all Microsoft services” to prevent removing critical Windows services. Click “Disable all” to turn off all non-Microsoft services running during launch. Then, on the “Startup” tab, select “Open Task Manager.”
- Disable all launch programs in Task Manager by choosing each and clicking “Disable.” Return to the System Configuration window after closing Task Manager. Click “OK” and then “Restart” to save your changes and restart your computer.
Run Power Troubleshooter
Running the Power Troubleshooter, an automated program within the Windows operating system meant to help users debug power-related issues, can help alleviate high power usage by Windows Explorer. You can find and repair any power-related problems causing excessive CPU usage.
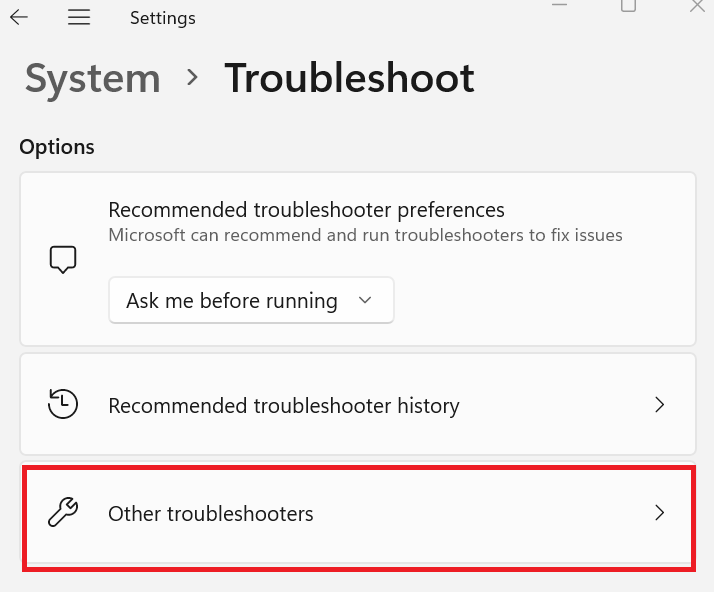
- To start, open the Windows Settings app, press the “Windows key + I” combination. Go to the Settings app and select “System.”. In the left sidebar, select “troubleshoot.” Scroll down to the right side and click on the “other troubleshoot” link.
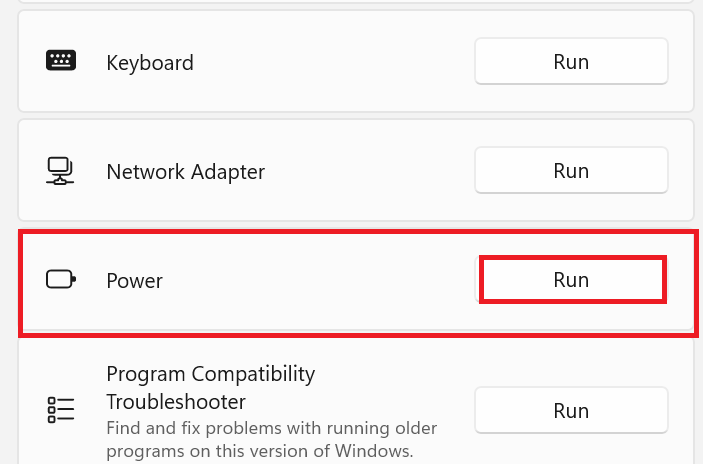
- This will launch the troubleshooting options dialogue box. At last, scroll down and look for the Power Option. Then click on the “run” button near the power option.
Lastly, Windows will launch the Power Troubleshooter to look for power-related issues. If the troubleshooter discovers any problems, it will provide you with information on how to fix them. To apply the recommended adjustments, follow the steps.
Unlink Your Onedrive Account
You can minimize the CPU burden on Windows Explorer and enhance overall system efficiency by unlinking your OneDrive account. It prevents constant file synchronization between your machine and the cloud storage service. OneDrive constantly checks for changes in files and syncs them in the background.
- If your OneDrive is currently syncing files, you may want to suspend the sync briefly. You must right-click the OneDrive icon in the system, select “More,” and then “Pause syncing.” Choose how long you want to pause the sync.
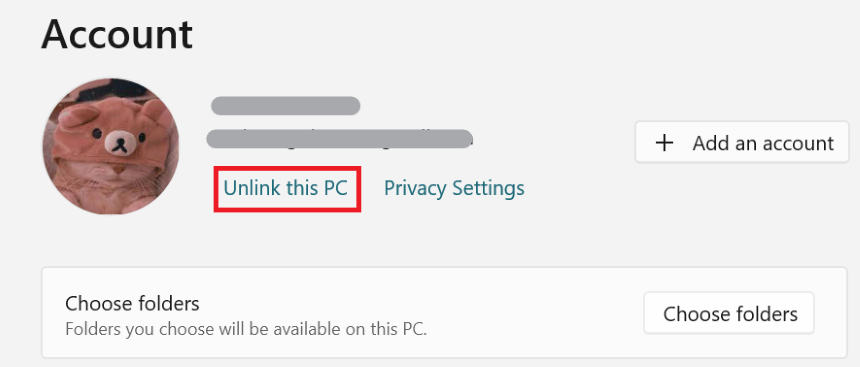
- To access the OneDrive menu, click the OneDrive icon in the system. Click on your account’s profile photo or initials in the top-right corner. From the drop-down menu, choose “Settings.” After that, navigate to the “Account” tab in the Microsoft OneDrive window.
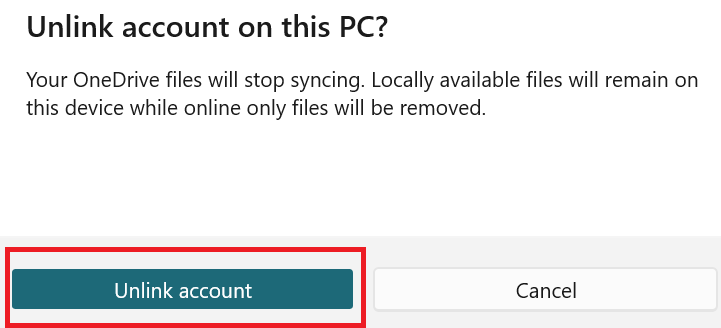
- Depending on the version of OneDrive you’re using, click “Unlink this PC” or “Unlink account.” Confirm your choice by selecting “Unlink account” or “Unlink.” If you wish to sign out of OneDrive altogether, go to the OneDrive menu, click on your account profile image or initials, then pick “Sign out.”
Rebuild Windows Search Index
Rebuilding the Windows Search Index can alleviate indexing issues and refresh the index database, which causes Windows Explorer to use too much CPU. The Windows Search Index controls fast file searches in File Explorer. Windows Explorer’s performance may suffer if the index gets corrupted or obsolete.
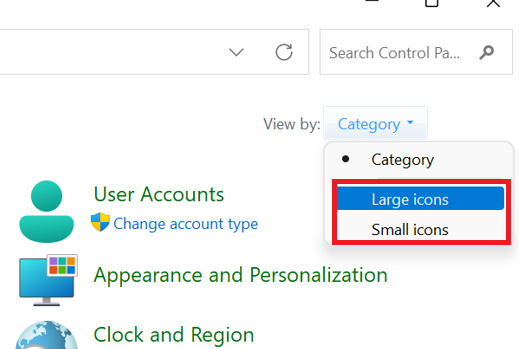
- To begin, open the Run dialogue box, and press the “Windows key + R” combination. To open the Control Panel, type “control” and hit Enter. Set the view in the Control Panel to “Large icons” or “Small icons.” And then, Select “Indexing Options.”
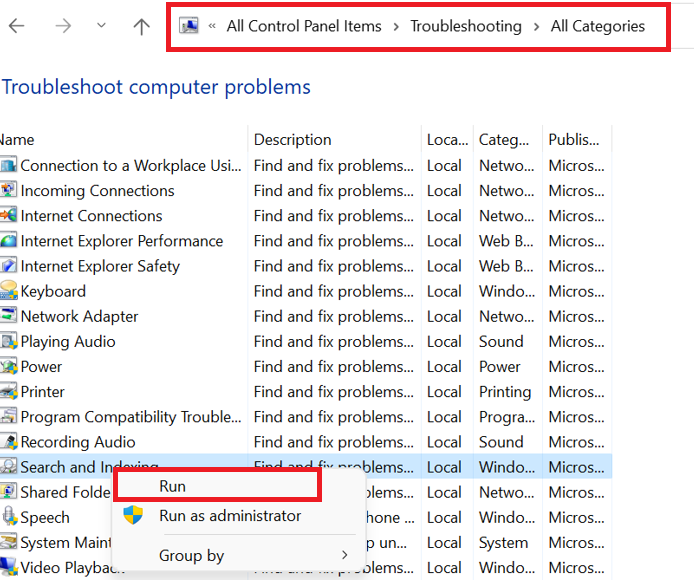
- Then go to the “Advanced” button in the Indexing Options window. And navigate to the “Troubleshooting” area of the Advanced Options box. Afterward, go to the “all category” option and select the “search and index” option. If you choose to rebuild the index, a confirmation notice will display. Select “run.”
The indexing process will begin, and depending on the size of your files and the number of objects indexed, it may take some time to complete. Allow it to complete the process. When the rebuild is complete, a notification will appear stating that the index has been rebuilt.
Perform a System Restore
System Restore will undo any system modifications that have caused the CPU use problem, like updates, driver installations, and software installations. If the problem was caused by recent updates, executing a System Restore should help restore Windows Explorer functionality.
- First, open the Run dialogue box by clicking the “Windows key + R” combination. Enter “rstrui” into the search box. This will launch the System Restore dialogue box. To begin, click “Next” in the System Restore window. You see the list of available restoration points. These are the dates on which your system was backed up, either automatically or manually.
- Then select a restore point before starting the high CPU utilization problem in Windows Explorer. To proceed, use the “Next” button. Examine the selected restore point and the programs that will be affected before proceeding. To confirm the restore point selected, click the “Finish” button.
- Finally, you will be warned that the System Restore cannot be stopped once it has begun. Check that you have saved any open work, then click “Yes” to proceed. Hence your computer will restart, and the System restore process will begin.
Furthermore, the System Restore process may take some time. During the procedure, your computer will restart several times. Thus Allow the restoration process to complete without interfering.
Check for Windows Updates
To update your windows go to the settings. Updates frequently include bug fixes, speed improvements, and optimizations. Windows updates address these issues of underlying system faults or vulnerabilities by delivering patches and improvements that can improve system functions, including Windows Explorer.
- Press the “Windows key + I” combination to open the Windows Settings app. You must go to the Settings app and select “Update & Security.” Navigate to the “Windows Update” tab on the left sidebar of the Update & Security window. Lastly, select the “Check for updates” option. Windows will begin searching for updates.
Depending on your internet speed and the number of updates available, this process may take some time. If updates are discovered, click the “Install” button to start the installation process. Windows will automatically download the updates. During the installation, your computer may restart.
Updates frequently address performance issues and security flaws that can jeopardize system stability. Remember that Windows updates are critical for preserving your computer’s security and efficiency. For a trouble-free experience, check for updates frequently and activate automatic updates.
What is the Normal Memory Usage for Windows Explorer?
Under normal circumstances, Windows Explorer typically occupies a memory range from 20 MB to several hundred megabytes. This memory consumption is influenced by factors inherent to your system’s configuration, usage patterns, system settings, and the number of open folders and files.
Because Windows Explorer is an essential component of the Windows operating system that is in charge of file management and user interface, it will require memory to navigate and show file information efficiently. If you open a lot of folders with a lot of files or if you run numerous instances of Windows Explorer at the same time, your memory use will rise proportionately.
Adding on, It is deemed typical as long as Windows Explorer’s memory utilization is within a tolerable range and does not cause performance difficulties or extreme system slowdowns. However, if Windows Explorer continually consumes an unusually large amount of RAM, this may signal a problem that needs further investigation to optimize system efficiency.
How to Monitor CPU Utilization By Windows Explorer?
The Windows Task Manager monitors CPU utilization and identifies the process or task that consumes a lot of CPU. Once you’ve determined the root reason, you can take suitable steps to restore normal CPU utilization, like updating software, running scans, or deactivating superfluous extensions.
- Here’s how to do it: right-click on your screen’s taskbar and select “Task Manager.” Alternatively, you can access Task Manager by pressing “Ctrl + Shift + Esc.” To examine the list of ongoing processes in the Task Manager window, click the “Processes” tab.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list and look for “Windows Explorer” or “explorer.exe .” It is generally near the top of the page under the “Apps” section. The proportion of CPU utilization by Windows Explorer may be found in the “CPU” column. The percentage reflects how much of the CPU’s processing power Windows Explorer uses now.
The CPU consumption of Windows Explorer can be tracked over time since the numbers in the “CPU” column change dynamically. You can also use Task Manager to see if any other apps or background processes contribute to high CPU consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Windows Explorer’s high CPU utilization can cause system slowdowns, unresponsiveness, and decreased overall efficiency. Throughout the debate, we discovered numerous probable causes for this problem and proposed practical strategies to solve it correctly.
The operation of resource-intensive tasks such as background processes, third-party shell extensions, malware infections, corrupted system files, and big media files is one of the primary causes of excessive CPU consumption. Also, we have given many actionable strategies to address these challenges. Running the Power Troubleshooter can assist in identifying and resolving power-related issues.
Furthermore, checking for Windows updates is crucial since updates include bug fixes and performance improvements that can improve Windows Explorer’s operation. Unlinking your OneDrive account or disabling cloud storage clients might reduce CPU strain by eliminating background file synchronization.
Moreover, restoring the system to a previous stable state or rebuilding the Windows Search Index can resolve issues caused by recent updates or indexing issues. Clearing damaged files with Command Prompt and deactivating recent items in File Explorer are other techniques that can improve CPU performance.

Hey, I’m Hammad. I write for this website to help you with the IT advice about PC, RAM, CPU, Motherboard, PSU, and other PC components.
I will provide detailed guides with images, and explain step by step so you can understand the process. Check all my articles here.